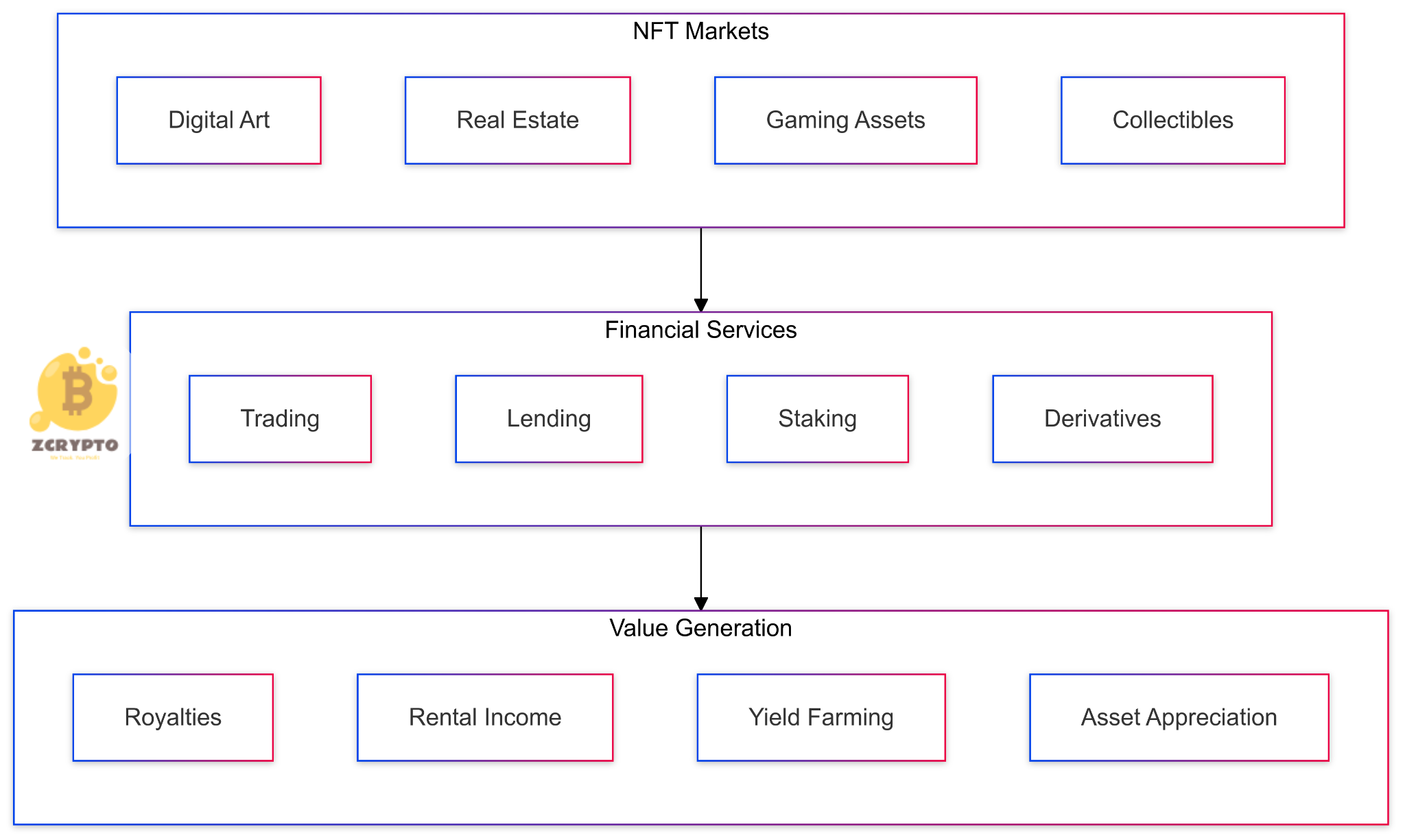
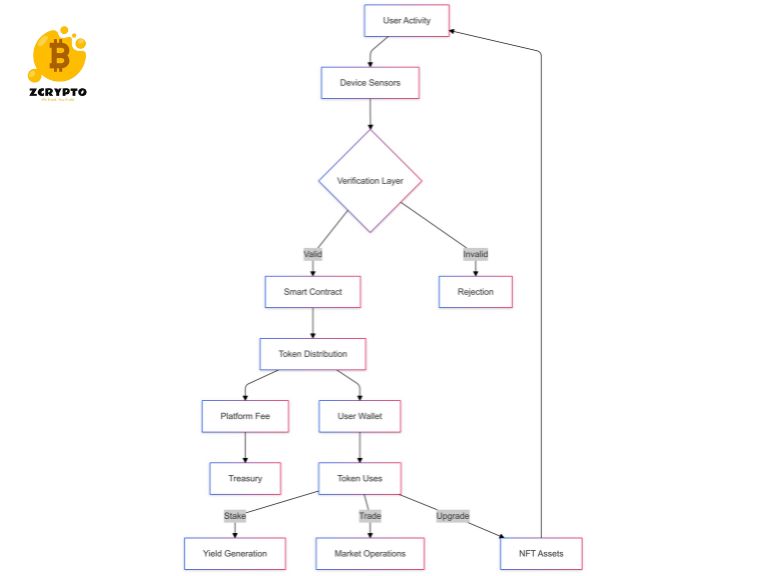
The financial mechanisms underlying NFT markets operate through sophisticated protocols and smart contracts. These systems facilitate value transfer, price discovery, and asset management across decentralized networks. Through automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools, NFT finance platforms enable fractional ownership, lending, and collateralization of digital assets.
Major NFT marketplaces implement dynamic pricing models based on supply-demand metrics, transaction volumes, and market sentiment indicators. These pricing mechanisms incorporate real-time data feeds and oracle networks to maintain accuracy and prevent market manipulation. For example, OpenSea’s pricing algorithm analyzes historical sales data, current market conditions, and comparable asset values to suggest optimal listing prices.
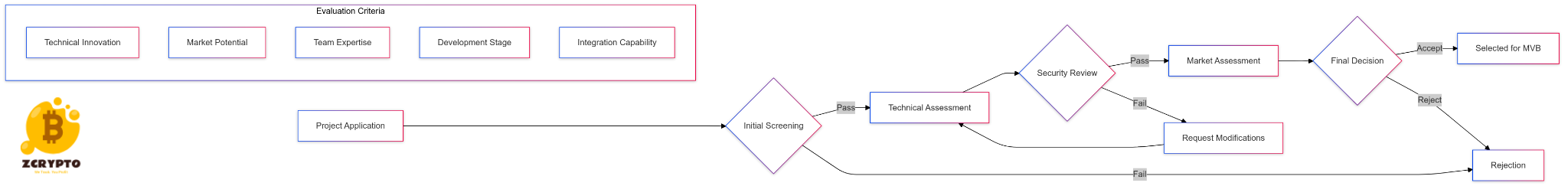
NFT finance platforms have developed specialized protocols for asset valuation. These protocols consider factors such as scarcity, utility, creator reputation, and market liquidity. The implementation of these protocols has led to more efficient price discovery and reduced information asymmetry between buyers and sellers.
Technical Infrastructure
The technical foundation of NFT finance rests on interoperable blockchain networks and smart contract standards. The ERC-721 and ERC-1155 token standards serve as the primary frameworks for NFT creation and exchange. These standards enable consistent asset representation and transfer across different platforms and marketplaces.
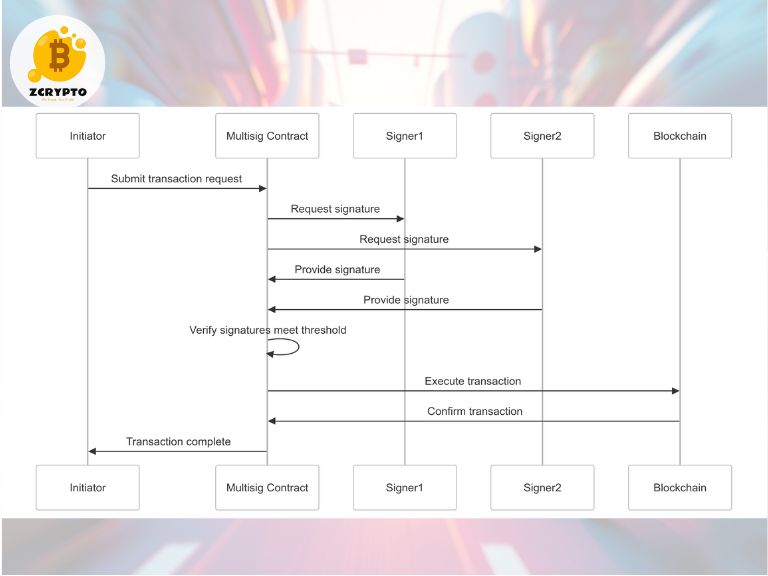
Smart contract architectures in NFT finance implement advanced security measures, including multi-signature authentication, time-locked transactions, and automated escrow systems. These technical safeguards protect against unauthorized transfers and smart contract vulnerabilities. Leading platforms employ formal verification methods to validate smart contract functionality before deployment.
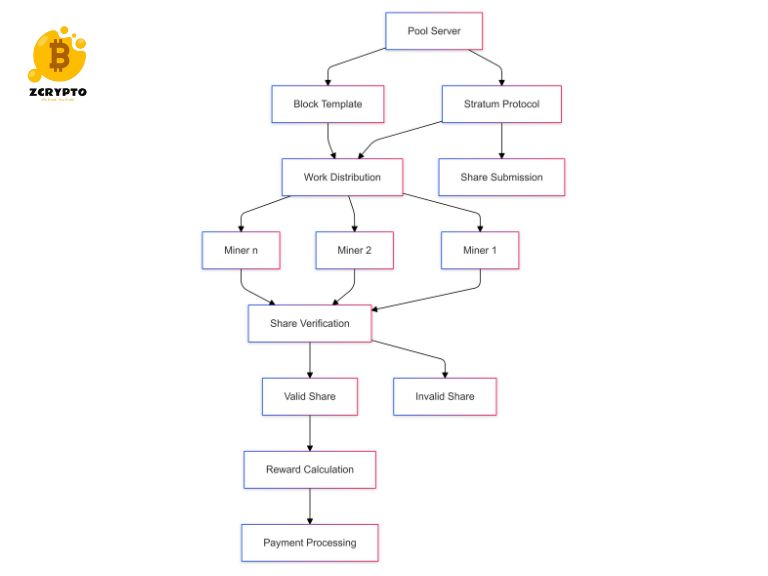
Cross-chain bridges and layer-2 scaling solutions address the scalability challenges in NFT finance. Networks like Polygon and Optimism reduce transaction costs while maintaining security through innovative rollup technology. These solutions have significantly improved transaction throughput and reduced gas fees for NFT trading.
Economic Implications
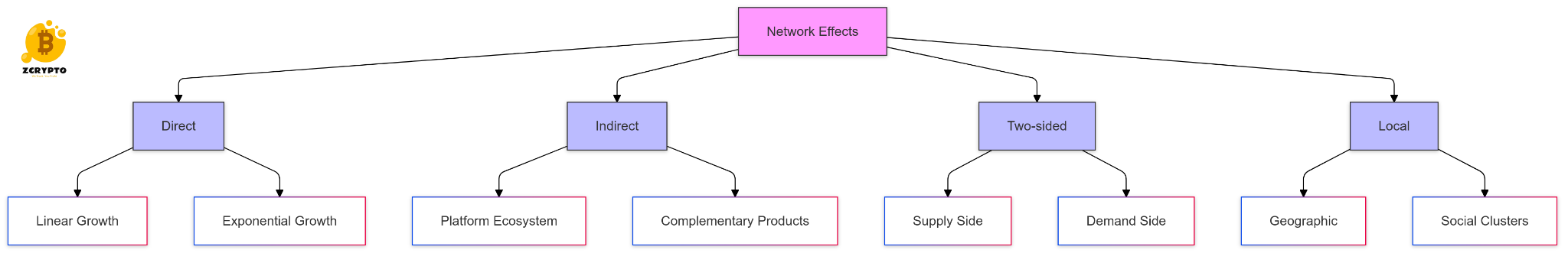
NFT finance introduces new economic models that challenge traditional asset management paradigms. The ability to fractionalize ownership of high-value assets has democratized investment opportunities and increased market liquidity. This transformation has created new revenue streams for creators and collectors while reducing barriers to entry for retail investors.
Risk management in NFT finance requires sophisticated approaches to address market volatility and liquidity risks. Platforms implement circuit breakers, insurance pools, and collateral requirements to protect stakeholders. Statistical models track market indicators to identify potential risks and trigger appropriate protective measures.
The integration of NFT finance with traditional financial systems has led to innovative hybrid products. These include NFT-backed loans, yield-generating NFT pools, and NFT-based derivatives. Financial institutions have begun incorporating NFT assets into their portfolio management strategies, recognizing their potential for diversification.
Practical Use Cases
Real estate tokenization through NFTs has enabled fractional property ownership and streamlined property transactions. Companies like RealT have successfully tokenized residential properties, allowing investors to purchase shares of real estate assets with minimal capital requirements. This model has reduced transaction costs and increased market accessibility.
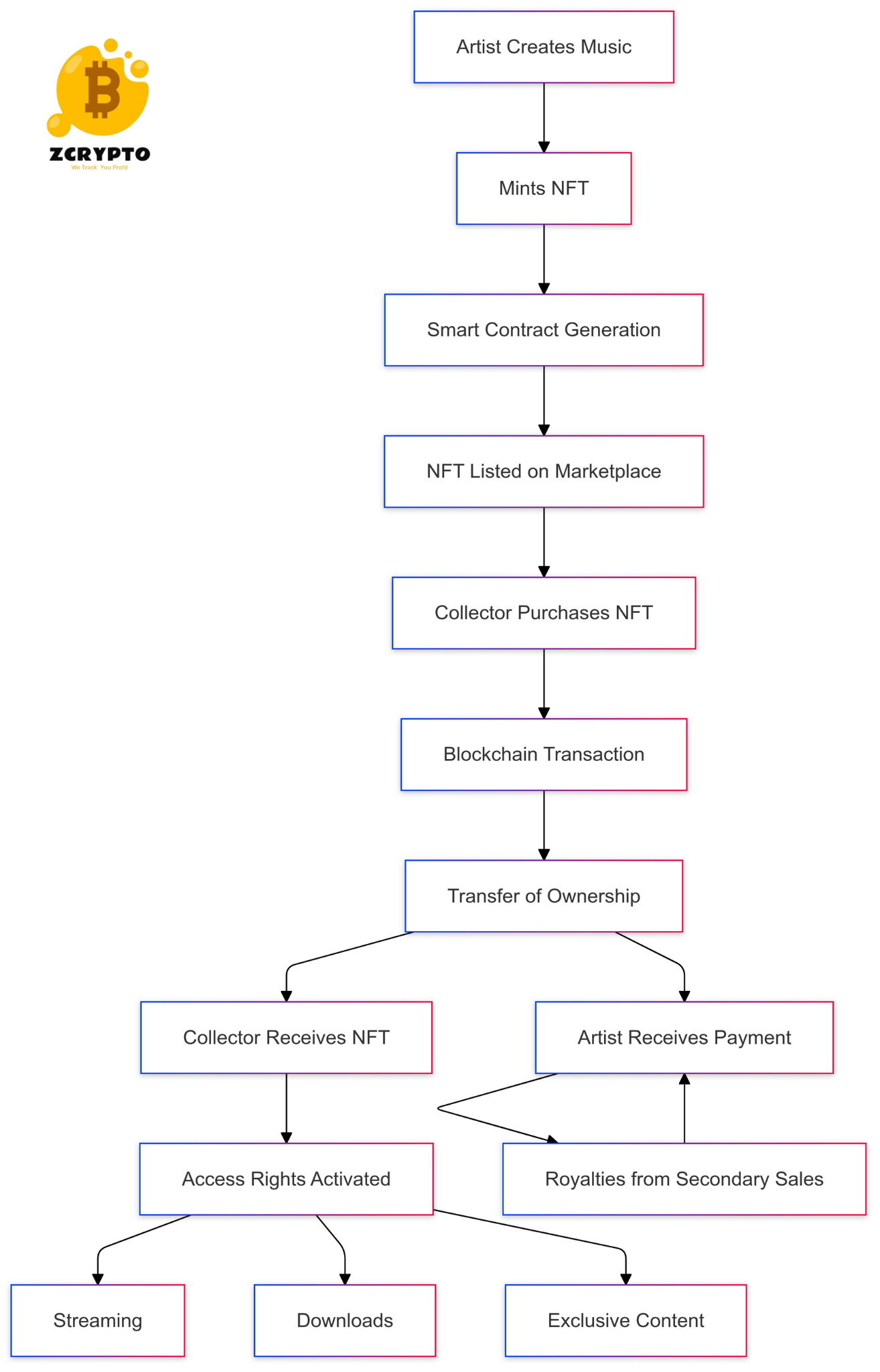
The art market has experienced significant transformation through NFT finance platforms. Christie’s and Sotheby’s have integrated NFT auctions into their traditional sales channels, reaching new audiences and achieving record-breaking sales. Digital artists have established sustainable revenue streams through programmable royalties on secondary sales.
Gaming economies leverage NFT finance for in-game asset trading and play-to-earn mechanisms. Games like Axie Infinity demonstrate how NFT-based assets can create real economic value for players. The integration of NFT finance has enabled new business models in gaming, including scholarship programs and asset lending systems.
Comparative Analysis
Traditional financial systems rely on centralized intermediaries and manual processes for asset transfer and verification. NFT finance eliminates these intermediaries through automated smart contracts, reducing costs and processing time. This automation has decreased settlement periods from days to minutes.
NFT finance platforms offer programmable ownership rights and automated royalty distribution, features absent in traditional systems. These capabilities enable creators to maintain ongoing revenue streams from their work. The transparent nature of blockchain technology provides immutable transaction records and clear provenance tracking.
The cost structure of NFT finance differs significantly from traditional models. While blockchain transactions incur gas fees, they eliminate many traditional administrative costs. Market participants benefit from reduced intermediary fees and increased transparency in pricing mechanisms.
NFT finance represents a fundamental shift in asset management and ownership models. The combination of blockchain technology, smart contracts, and innovative financial protocols has created new opportunities for value creation and exchange. The practical applications across real estate, art, and gaming demonstrate the versatility and potential of NFT-based financial systems.
The development of robust technical infrastructure and standardized protocols continues to strengthen the foundation of NFT finance. As markets mature and adoption increases, the integration with traditional financial systems will likely deepen, leading to more sophisticated financial products and services.








Leave a Reply